What Are Registers In Comuting
CPU Registers
What Are CPU Registers ?
Computer Organization And Architecture
The registers are an important component of the processor's micro-architecture. The registers are the loftier speed memory built into the CPU chip for quick data access. Information technology is as well the fastest retentiveness in the memory hierarchy.
The register effectively functions equally high speed temporary retentiveness used by the CPU ( a microprocessor chip ) during the program execution. Depending upon the CPU micro compages, the processor can have many registers.
The CPU micro architecture consists of unlike types of registers. Each of these register performs a specific function during the various stages of the didactics bicycle.
| Register Symbol | Register Name | Bit Size | Register Role |
| Air-conditioning | Accumulator | sixteen Bits | Stores Data For ALU Operations |
| PC | Programme Counter | 12 Bits | Points To Adjacent Instruction |
| IR | Instruction Register | xvi Bits | Stores Instruction |
| DR | Data Register | 16 Bits | Stores Data |
| AR | Accost Register | 12 Bits | Stores Accost |
| TR | Temporary Register | 16 Bits | Stores Temporary Data |
| INTR / OUTR | Input And Output Registers | Each 8 Bits | Stores Input And Output Data |
The educational activity cycle is the basic function of the CPU repetitively performed to execute the program. The educational activity cycle is a continuous CPU functioning. It is too referred as Fetch Decode and Execute wheel.
The CPU needs access to high speed retentiveness during the various stages of the instruction bike. The registers are used by the CPU equally high speed temporary storage during the programme execution.
In this article, y'all will learn what are cpu registers, dissimilar types of registers and their functions and other related important concepts.
The registers are an important component of the CPU. So , permit us first starting time with a brief introduction to the central processing unit of measurement ( CPU ).
What Are CPU Registers ?
Tabular array Of Contents
What Are CPU Registers ?
The registers are high speed retention placed inside the processor chip that provides quick data access to the CPU. The chief role of the processor is to execute the program instructions.
The program instructions are stored into the main memory RAM ( Random Access Retentivity ) during the program execution.
The operating system loads the program instructions and the information into the memory. The processor retrieves the data and instructions from the main retention RAM 1 by one.
Hither is an case of the different types of registers used in the Intel 8085 Compages.
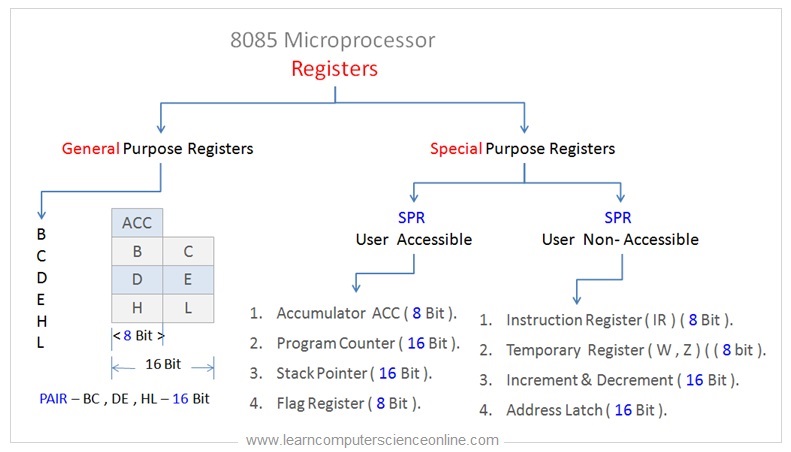
The processor micro architecture consist of different types of registers. Each register is used past the CPU at unlike stages of the didactics bicycle.
The register is a internal loftier speed retentiveness of the processor. It is the smallest in size but fastest in the memory hierarchy.
In digital electronics, a register is a group of flip-flops that can shop i bit of data. A flip flop is a latch blazon circuit that has two stable states that can exist used to shop the binary data ( zero 0 or ane 1 ).
The register consist of group of flip flops and the logic gates. In register the, the flip-flops holds the binary data and the logic gates controls the flow of information into the register.
What Are CPU Registers ?
What Is CPU ?
Central Processing Unit ( CPU )
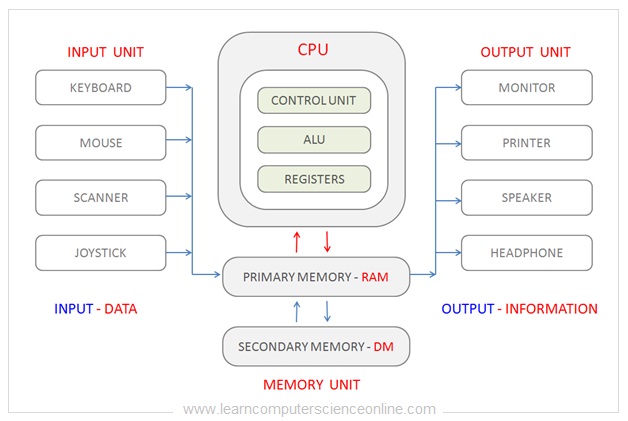
The CPU stands for cardinal processing unit of measurement. It is the main component placed on the motherboard that provides the necessary processing ability to the calculator organization.
The CPU is also alternately referred to as processor, microprocessor or processing unit of the computer system.
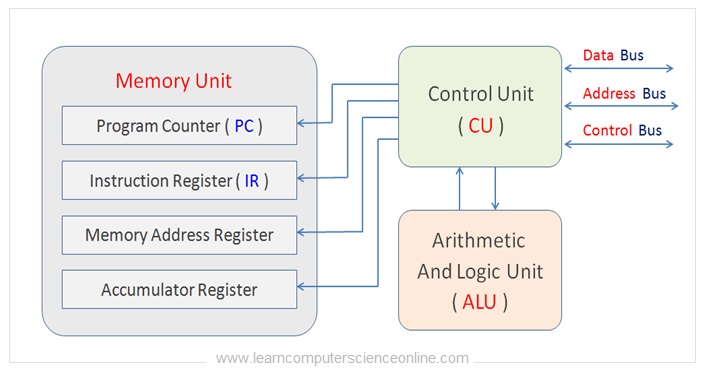
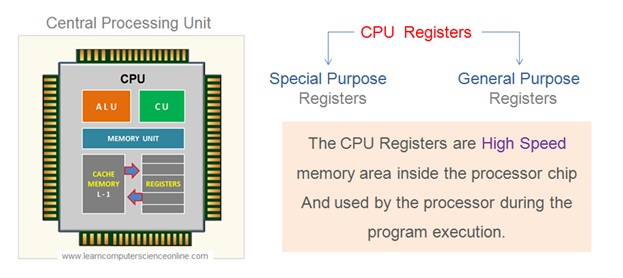
The CPU internally consist of three important units. These units are arithmetic and logic unit of measurement ( ALU ) , Control Unit ( CU ) and the memory unit ( MU ).
The registers are part of the memory unit of measurement of the CPU. The ALU performs the arithmetic and logical operations.
The processor micro architecture consist of different types of registers. Each register is used by the CPU at different stages of the instruction cycle.
The annals is a internal high speed retentiveness of the processor. It is the smallest in size only fastest in the memory bureaucracy.
What Are CPU Registers ?
Registers And Memory Hierarchy
The registers are the smallest simply the fastest component of the retention hierarchy used in the reckoner compages. The registers are part of the internal temporary storage used past the CPU.
The CPU's execution speed is very high. Whereas, the main memory RAM cannot friction match the execution speed of the CPU.
And therefore, high speed memories are placed between the CPU and the main memory RAM to improve the organization performance.
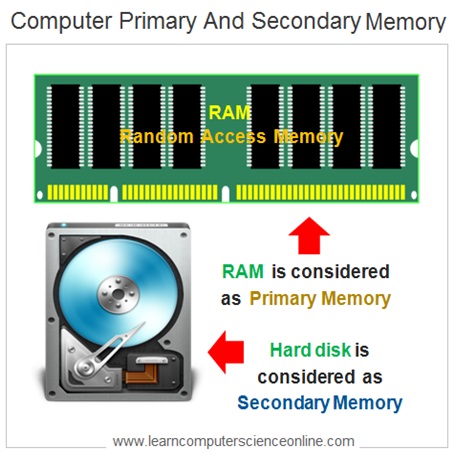
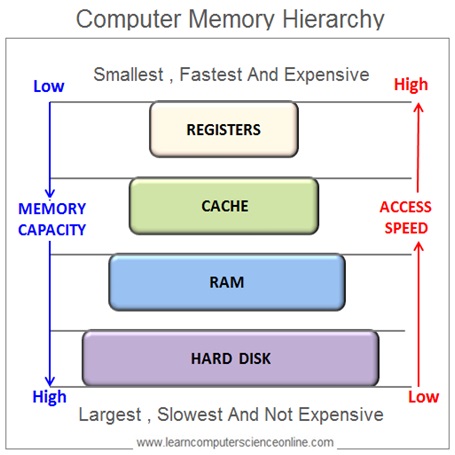
The memory hierarchy includes secondary disk retentiveness , primary main retentiveness RAM , cache memory ( L1, L2 And L3 Cache memory ) and the registers.
The secondary memory ( disk memory ) is the largest in size just provides lowest information admission speed. The registers are the smallest in size just provides the fastest data access speed.
What Are CPU Registers ?
Types Of CPU Registers
Depending upon the CPU's micro compages , the CPU tin accept different types of registers. The dissimilar types of CPU registers include :
The CPU registers tin can be broadly split into two types. The first blazon of CPU registers are full general purpose registers and the second type is special purpose registers.
The CPU registers can either exist programmer accessible and some registers are non-accessible registers to the developer. Let the states talk over each register types in item.
Depending upon the CPU's micro compages , the CPU tin can have different types of registers. The different types of CPU registers include :
| Annals Symbol | Annals Proper noun | Scrap Size | Annals Office |
| Air conditioning | Accumulator | sixteen Bits | Stores Data For ALU Operations |
| PC | Program Counter | 12 $.25 | Points To Side by side Instruction |
| IR | Instruction Register | sixteen Bits | Stores Instruction |
| DR | Information Annals | xvi $.25 | Stores Information |
| AR | Address Annals | 12 Bits | Stores Accost |
| TR | Temporary Register | xvi Bits | Stores Temporary Data |
| INTR / OUTR | Input And Output Registers | Each 8 Bits | Stores Input And Output Data |
The CPU registers can be broadly divide into two groups. The showtime group is general purpose registers ( GPR ) and the second group is special purpose registers ( SPR ).
What Are CPU Registers ?
CPU Register Sizes
The size of the register is measured by the number of bits. The about common register size include 8 chip register, 16 scrap register, 32 chip annals and 64 bit annals.
The standard register naming convention to access the register depends upon the size of the register.
In computing , a byte addressable retention organization refers to the size of the memory address register. For example, In a 32-bit computer, the CPU can address 2 to the ability 32 = 4,294,967,296 bytes of memory. That is equal to RAM memory size of 4 Gigabyte.
General Purpose Registers
The general purpose registers ( GPR ) are used in CPU architecture for either storing the information , memory addresses or instructions. The processor contains number of full general purpose registers.
The full general purpose registers are named registers ( R1 , R2 , R3 , …. , Rn ). The memory locations are accessed by its address. Whereas, the registers are accessed by its proper noun.
The register naming convention ( identifiers ) used to access the registers depends upon the size of the annals. The register size is measured in bits.
The general purpose registers tin can be accessed in the plan by using depression level assembly level programming.
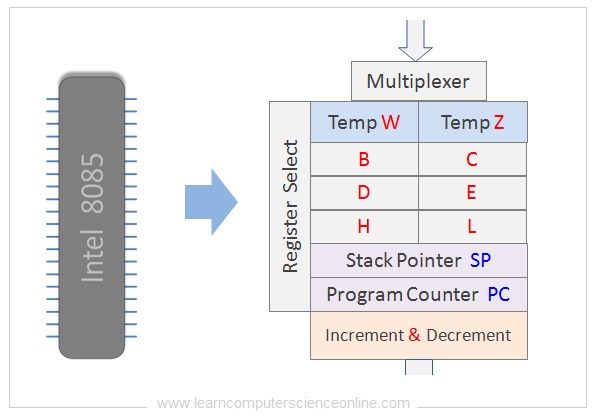
The implementation of the full general purpose registers ( GPR ) depends upon the processor compages. Here is an example of GPR in Intel 8085 architecture.
What Are CPU Registers ?
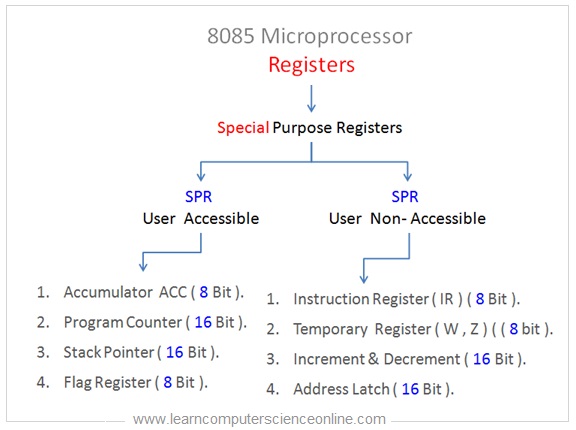
Special Purpose Registers
Every bit the name suggest, the special purpose registers have special designated purpose. The special purpose registers can be used by the CPU only for the specified performance.
For case, the program counter register is a special purpose register. The programme counter register ever contains the address of the side by side didactics to exist fetched and that cannot exist modified by programmer.
Similarly, the instruction register is another special purpose register. The instruction register always holds the instruction fetched from the retentivity.
The command units decodes the machine education stored into the didactics register as per the instruction format.
Plan Counter Register
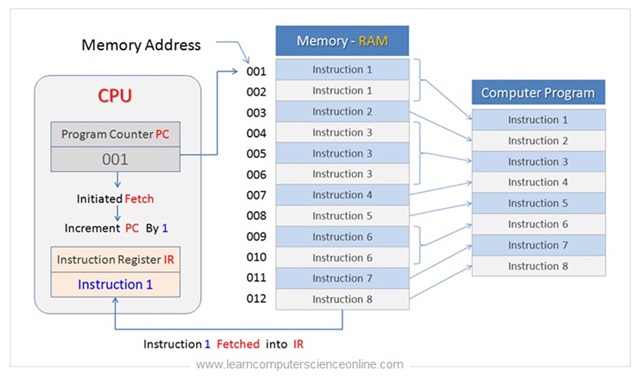
The program counter register ( PC ) is a special purpose register used past the CPU to store the address of the side by side instruction to be executed.
The program counter register is automatically incremented by one after the fetching the terminal instruction so that it ever points to the address of the next educational activity.
A program counter is also alternately referred to as an didactics counter, instruction pointer, didactics address register or sequence control register. The PC annals keeps the track of the execution sequence of the CPU.
What Are CPU Registers ?
Educational activity Register
In society to execute the program, the CPU repetitively performs the instruction cycle. The fetch performance is the first step of the didactics wheel.
The instructions are stored into the main retentiveness RAM. The CPU fetches these instructions ane past 1. The program educational activity is stored into the instruction register afterward it is fetched by the CPU.
Information technology is the control unit that decodes the program machine instruction. The control unit of measurement decodes the instruction as per the instruction format.
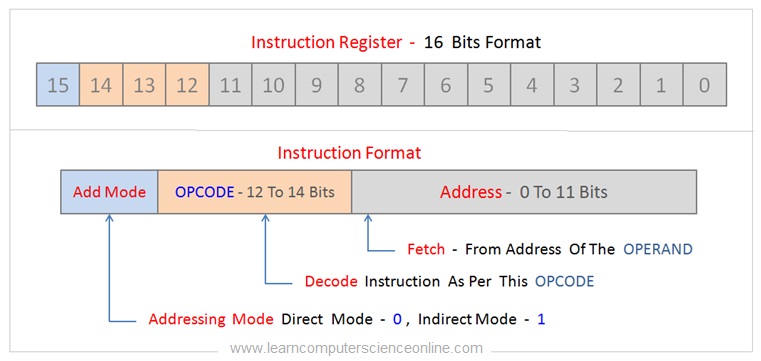
The instruction format typically has three parts. The operand function indicates either information or the address of the data. The opcode stands for operation code that defines the operation to be performed and the addressing.
The addressing mode part of the didactics format defines the either direct referencing or indirect referencing.
For indirect referencing , the operand value contains the retention address or effective accost of the operand.
What Are CPU Registers ?
Accumulator Register
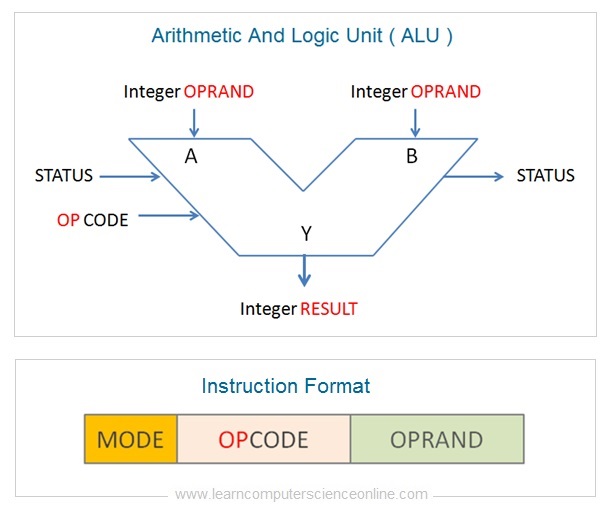
The accumulator register is used by the ALU ( arithmetic and logic unit ) to perform the arithmetics and the logical operations performed by the CPU.
The ALU operates on the data stored into the accumulator annals. After the ALU operation, the processed data is either sent to the primary memory RAM or to the output device.
The primary purpose of the accumulator is to provide high speed memory for various ALU operations.
A CPU organization is said to exist a unmarried accumulator blazon when information technology has merely one unmarried accumulator . Notwithstanding, modern CPU can accept number of general purpose registers tin can be used by the CPU as accumulator.
Address Annals
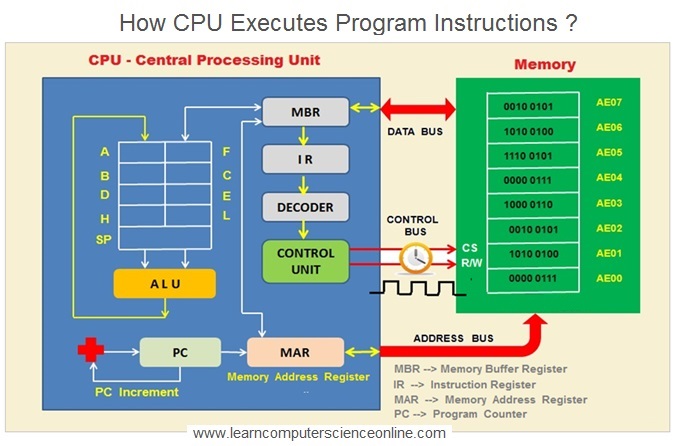
Retentivity Address Annals ( MAR )
The retentivity address register ( MAR ) is also called equally address register. The memory address annals ( MAR ) essentially contains the memory address from where the CPU either needs to fetch the data or write the data.
During the plan execution, the CPU performs the memory read and write operations at specific memory address. This accost is stored in the MAR.
The memory address register is used by the CPU while performing the input and output operations. The retentivity address register specifies the memory address either for retentiveness read or retention write performance.
What Are CPU Registers ?
Data Register
Memory Buffer Register ( MBR )
The memory buffer register ( MBR ) is also called every bit data register. Information technology essentially contains the data that CPU either has to fetch from the retention. The data register is likewise used when the CPU needs to write into the retentiveness at the address specified in MAR.
During the plan execution, the CPU performs the memory read and write operations at specific retention address. This data is stored in the MBR.
The retentivity buffer register is used past the CPU while performing the input and output operations. The memory buffer register stores the data fetched by the CPU during the retention read performance or the data for memory write operation.

Input Annals
In some programs the user inputs the data that is processed by the computer. In reckoner architecture this information is temporarily stored into the input register.
The input register ( INPR ) is a 8 bit register that stores the alphanumeric input data. The contents of the input register is transferred to the accumulator ( Air conditioning ) where ALU operates on the data.
Output Register
Similarly , the CPU operates on the program data as per the program instructions. The processed data is stored in the output register ( OUTR )
The contents of the accumulator ( Air conditioning ) are transferred to the output register after the ALU operation .
The data from the output register is and so sent to the main memory RAM . The operating system then sends the data to the output device.
What Are CPU Registers ?
Temporary Register
The temporary registers are general purpose registers used by the CPU during the plan execution to temporarily store the data.
The temporary register is a 16 bit register used by the CPU for the temporary storage of data.
Computer Science Online Course


What Are Registers In Comuting,
Source: https://www.learncomputerscienceonline.com/what-are-cpu-registers/
Posted by: alcarazderming.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are Registers In Comuting"
Post a Comment